Whether cuttings or germination, these two steps mark the start of your indoor cultivation.
Cutting involves preserving the genetics of an existing plant by cloning it.
Germination simply means starting a new crop from scratch.

What is germination?
It's all about germinating your seeds with a little heat, darkness and water. As a beginner grower, this is most likely how you'll start your first crop. You'll discover that, just as every human being is unique, every plant has its own genetics, even within the same family. You'll need to learn to recognize the genetics that best match your expectations, so as to create mother plants that will enable you to conserve these genetics.
Germination techniques
You may not know it, but putting a seed in the ground is not the only way to germinate it. In fact, it's one of the least effective methods, as it prevents you from checking whether the seed has opened properly on contact with water. Nevertheless, a seed needs 3 essential elements to germinate: humidity, a temperature between 20°C and 30°C and darkness.
What is the plate technique?
Place your seeds on a plate between two damp sheets of kitchen paper. Then close the whole thing with a second plate to immerse your seeds in the dark. Make sure the paper stays moist until germination takes place, after 2 to 10 days, depending on the plant. This old-fashioned method has proved its worth. Be careful, however, that the cotton fibres on the paper don't catch on the plant's first rootlets when you place your seed in your growing space.
The glass-of-water technique?
This is probably the simplest and most effective technique. Place your seeds in a glass of water. At first, your seeds will float. When they open up, they'll sink, so you can plant them in your growing space.

Other germination techniques?
There are products designed to encourage seeds to germinate in such a way as to trigger explosive growth. This is the case, for example, with Dynamite seed. This is a mycorrhizal powder containing 500 propagules per gram of a fungus called Glomus intraradices. Its function is to facilitate exchange between the nutrient solution, the plant and the soil. This seed-coating powder will also enable you to germinate your seeds more quickly.
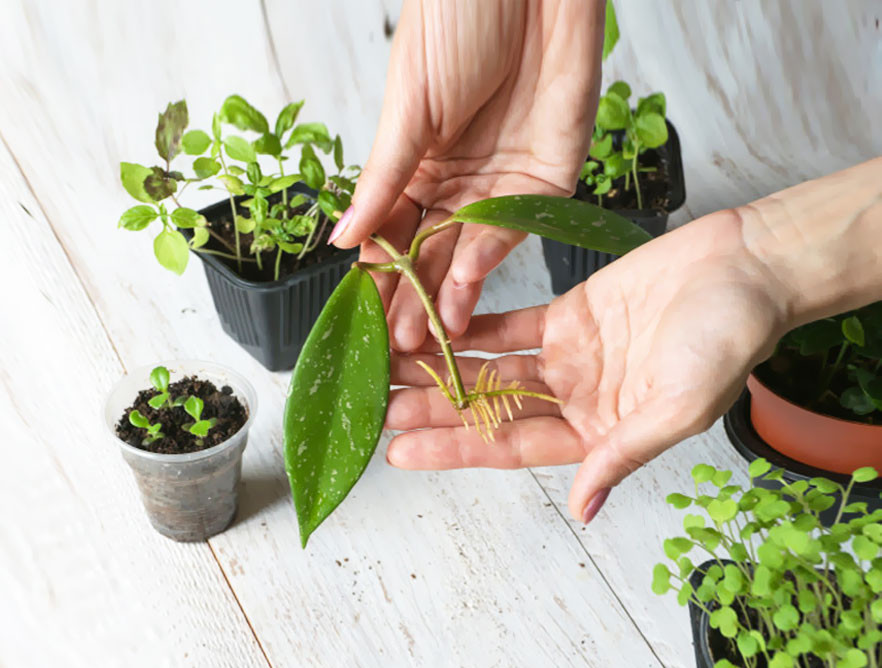
What is cuttings?
Cutting consists, as explained above, in cloning the plant whose genetics you want to preserve according to the criteria of your choice. In this way, you can achieve a more organized culture, with each plant identical to its neighbor if you treat them all in the same way. Another important aspect of cuttings is that you know the sex of your plant in advance.
Cutting technique
There are no 50 techniques for taking cuttings. There are, however, a few steps to follow:
- Choose a healthy mother plant and water it 2 days before taking the cuttings.
- Cut the branches back 10 to 15 cm using pruning shears or a specially disinfected scalpel.
- Remove the leaves and side shoots, keeping just 2 buds and bevelling the stem.
- Cut off any leaf tips to limit evapotranspiration.
- Dip your cuttings in a nutrient solution based on cuttings hormones or in clear water.
- Plant the cuttings in a special substrate such as coconut fibre or rock wool.
- Place your cuttings in a covered greenhouse to maintain maximum humidity, and water generously.

Now that you've got the basics down, all you have to do is get started!




